Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -octylnitrilo-triacetamide (HONTA) complexes of americium and europium
-octylnitrilo-triacetamide (HONTA) complexes of americium and europiumToigawa, Tomohiro; Peterman, D. R.*; Meeker, D. S.*; Grimes, T. S.*; Zalupski, P. R.*; Mezyk, S. P.*; Cook, A. R.*; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Kumagai, Yuta; Matsumura, Tatsuro; et al.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 23(2), p.1343 - 1351, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:81.5(Chemistry, Physical)The candidate An(III)/Ln(III) separation ligand hexa- -octylnitrilo-triacetamide (HONTA) was irradiated under envisioned SELECT (Solvent Extraction from Liquid waste using Extractants of CHON-type for Transmutation) process conditions using a solvent test loop in conjunction with cobalt-60 gamma irradiation. We demonstrate that HONTA undergoes exponential decay with increasing gamma dose to produce a range of degradation products which have been identified and quantified by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS techniques. The combination of HONTA destruction and degradation product ingrowth, particularly dioctylamine, negatively impacts the extraction and back-extraction of both americium and europium ions. The loss of HONTA was attributed to its reaction with the solvent (
-octylnitrilo-triacetamide (HONTA) was irradiated under envisioned SELECT (Solvent Extraction from Liquid waste using Extractants of CHON-type for Transmutation) process conditions using a solvent test loop in conjunction with cobalt-60 gamma irradiation. We demonstrate that HONTA undergoes exponential decay with increasing gamma dose to produce a range of degradation products which have been identified and quantified by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS techniques. The combination of HONTA destruction and degradation product ingrowth, particularly dioctylamine, negatively impacts the extraction and back-extraction of both americium and europium ions. The loss of HONTA was attributed to its reaction with the solvent ( -dodecane) radical cation of
-dodecane) radical cation of  (HONTA + R
(HONTA + R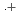 ) = (7.61
) = (7.61  0.82)
0.82)  10
10 M
M s
s obtained by pulse radiolysis techniques. However, when this ligand is bound to either americium or europium ions, the observed
obtained by pulse radiolysis techniques. However, when this ligand is bound to either americium or europium ions, the observed  -dodecane radical cation kinetics increase by over an order of magnitude. This large reactivity increase to additional reaction pathways occurring upon metal-ion binding. Lastly nanosecond time-resolved measurements showed that both direct and indirect HONTA radiolysis yielded the short-lived (
-dodecane radical cation kinetics increase by over an order of magnitude. This large reactivity increase to additional reaction pathways occurring upon metal-ion binding. Lastly nanosecond time-resolved measurements showed that both direct and indirect HONTA radiolysis yielded the short-lived ( 100 ns) HONTA radical cation as well as a longer-lived (
100 ns) HONTA radical cation as well as a longer-lived ( s) HONTA triplet excited state. These HONTA species are important precursors to the suite of HONTA degradation products observed.
s) HONTA triplet excited state. These HONTA species are important precursors to the suite of HONTA degradation products observed.
Department of Materials Science
JAERI-Review 2004-027, 131 Pages, 2004/12
This report is research activities using Tandem Accelerator in Tokai during April 1st in 2003 to March 31st in 2004, and contains 42 reports of 7sections of (1) operation and developments of tandem accelerator, (2) nuclear structure, (3) nuclear reactions, (4) nuclear chemistry, (5) nuclear theory, (6) atomic physics and solid state physics, (7) radiation effect of materials, and also contains of publication lists, personnel for related activities and the cooperation research program between JAERI and universities, national research organizations and so on.
Nakano, Junichi; Tsukada, Takashi; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Terakado, Shogo; Koya, Toshio; Endo, Shinya
JAERI-Tech 2003-092, 54 Pages, 2004/01
Irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) is a degradation phenomenon caused by synergy of neutron radiation, aqueous environment and stress on in-core materials, and it is an important issue in accordance with increase of aged light water reactors. Isolating crack initiation stage from crack growth stage is very useful for the evaluation of the IASCC behavior. Hence facility for in-situ observation during slow strain rate test (SSRT) for irradiated material was developed. As performance demonstrations of the facility, tensile test with in-situ observation and SSRT without observation were carried out using unirradiated type 304 stainless steel in 561 K water at 9 MPa. The following were confirmed from the results. (1) Handling, observation and recording of specimen can be operated using manipulators in the hot cell. (2) In-situ observation can be performed in pressurized high temperature water and flat sheet type specimen is suitable for the in-situ observation. (3) Test condition can be kept constantly and data can be obtained automatically for long test period.
Department of Materials Science
JAERI-Review 2003-028, 173 Pages, 2003/11
This annual report describes research activities which have been performed with the JAERI tandem accelerator from April 1, 2002 to March 31, 2003. Summary reports of 54 papers, and lists of publication, personnel and cooperative research with universities are contained.
Committee for the Joint Research Project between JAERI and Universities; Committee for the Universities' JAERI Collaborative Research
JAERI-Conf 2003-015, 103 Pages, 2003/11
The present report describes the Proceedings of the Symposium on the Joint Research Project between JAERI and Universities - Results of the 4th Phase Joint Research Project and the Future Plan -, held at the University of Tokyo on February 18, 2003. The joint research project composed of the backend chemistry project and the advanced radiation application project was to be concluded in the end of March 2003. Hence the symposium was held in order to review the results obtained in the 4th phase project and to exchange ideas on the effective measures for the future joint collaboration in view of the past activities.
Ikezoe, Hiroshi; Yoshida, Tadashi; Takeuchi, Suehiro
JAERI-Conf 2003-017, 175 Pages, 2003/10
The facility of the JAERI tandem accelerator and its booster has been contributing to advancing heavy ion science researches in the fields of nuclear physics, nuclear chemistry, atomic and solid state physics and materials science, taking advantage of its prominent performances in providing various heavy ions. This meeting, as well as the previous ones held twice, offered scientists from the fields of heavy ion science, including nuclear physics, solid-state physics and cross-field physics, an opportunity to have active discussions among them, as well as to review their research accomplishments in the last two years. Oral presentations were selected from a wider scope of prospective fields, expecting a new step of advancing in heavy ion science. Main topics of the meeting were the status of the JAERI-KEK joint project of developing a radioactive nuclear beam(RNB) facility and research programs related to the RNB.
Department of Materials Science
JAERI-Review 2002-029, 152 Pages, 2002/11
no abstracts in English
Baba, Yuji
Trends in Vacuum Science & Technology, Vol.5, p.45 - 74, 2002/10
This article reviews recent works on the ion desorption from solid surfaces induced by the irradiation of soft X-rays ranging from 100 eV to 3 keV. The data presented here are focused on the positive ion desorption from adsorbed, condensed, and solid molecules following the core-level excitations. The element-specific and site-specific fragment-ion desorptions are clearly realized, when we tune the photon energy at the core-to-valence resonance regions. The specificity of the ion desorption more clearly shows up following the deep-core excitations, i.e., 1s 4p resonant excitations in third-row elements, rather than the shallow-core excitations. Since the main decay channels after the core-level excitation are the Auger transitions, the Auger decay spectra excited by the photons around the core-level thresholds are also presented for some of the adsorbed systems. The mechanism of the observed highly specific ion desorption is discussed on the basis of the photon-energy dependencies of the electron and ion yields and the analysis of the Auger decay spectra.
4p resonant excitations in third-row elements, rather than the shallow-core excitations. Since the main decay channels after the core-level excitation are the Auger transitions, the Auger decay spectra excited by the photons around the core-level thresholds are also presented for some of the adsorbed systems. The mechanism of the observed highly specific ion desorption is discussed on the basis of the photon-energy dependencies of the electron and ion yields and the analysis of the Auger decay spectra.
Mori, Yuichiro*; Ide, Hiroshi; Nabeya, Hideaki; Tsukada, Takashi
JAERI-Tech 2002-003, 32 Pages, 2002/02
In relation to the aging of Light Water Reactor (LWR), the Irradiation Assisted Stress Corrosion Cracking (IASCC) has been regarded as a significant and urgent issue for the reliability of in-core components of LWR, and the irradiation research on the IASCC is now under schedule. With the progress of the irradiation research on reactor materials, well-controlled environment conditions during irradiation testing are required. Especially for irradiation testing of IASCC studies, water chemistry control is essential in addition to the control of neutron fluence and irradiation temperature.According to these requirements, at the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), an irradiation testing facility that simulates in-core environment of Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) has been designed to be installed in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). This facility is composed of the Saturated Temperature Capsules (SATCAP) that are installed into the JMTR's core to irradiate material specimens, the Water Control Unit that is able to supply high-temperature and high-pressure chemical controlled water to SATCAP, and other components.This report describes the design study of water chemistry control system of the Water Control Unit. The design work has been performed in the fiscal year 1999.
Department of Materials Science
JAERI-Review 2001-030, 147 Pages, 2001/11
no abstracts in English
HTTR Utilization Research Committee
JAERI-Review 2001-016, 232 Pages, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
Sudo, Yukio; Hoshiya, Taiji; Ishihara, Masahiro; Shibata, Taiju; Ishino, Shiori*; Terai, Takayuki*; Oku, Tatsuo*; Motohashi, Yoshinobu*; Tagawa, Seiichi*; Katsumura, Yosuke*; et al.
Proceedings of OECD/NEA 2nd Information Exchange Meeting on Basic Studies in the Field of High-temperature Engineering, p.39 - 50, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Baba, Yuji; Yoshii, Kenji; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Sasaki, Teikichi; W.Wurth*
Material Chemistry 96: Proc. of Int. Symp. on Material Chemistry in Nuclear Environment, 0, p.391 - 399, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Motoe; Furuta, Teruo
JAERI-M 92-162, 57 Pages, 1992/11
no abstracts in English
JAERI-M 92-129, 40 Pages, 1992/09
no abstracts in English
JAERI-M 91-054, 44 Pages, 1991/03
no abstracts in English
Takehisa, Masaaki*; *; Nagayama, Hisashi; Ono, Shinichi;
Hoshasen Kagaku No Rekishi To Mirai; 30-Nen No Ayumi, p.57 - 67, 1991/00
no abstracts in English
JAERI-M 90-054, 57 Pages, 1990/03
no abstracts in English
JAERI-M 88-272, 46 Pages, 1989/01
no abstracts in English